 |
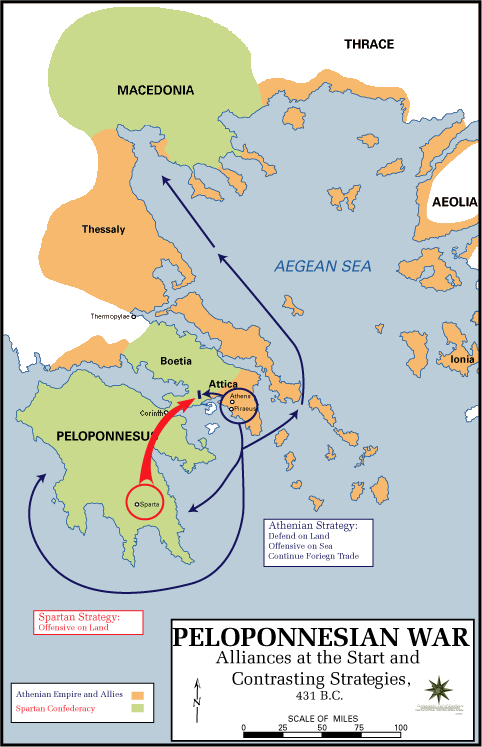
Peloponnesian war was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire
against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally
divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War,
Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of
its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese and attempt to
suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded
in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was
soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese.
|
 |
The Archidamian War is the name
of the first part of the Peloponnesian War
(431-404), the great conflict between Athens and Sparta. It is called after the
Spartan king Archidamus II. This war started in 431 and ended in 421 with
something that came close to an Athenian victory and a Spartan defeat.
However, Athenian diplomatic mistakes, Spartan intransigence, and a
catastrophic Athenian attempt to conquer the island of Sicily were enough to
change the balance of power, so that Sparta got a second chance: the Decelean
or Ionian War.
|
 |
Decelean War or Ionian War: name of
the last part of the Peloponnesian War (431-404). The first phase, the
Archidamian War, had ended in 421 with something that came close to an
Athenian victory. However, Athenian diplomatic mistakes, Spartan
intransigence, and a disastrous Athenian attempt to conquer the island of
Sicily changed the balance of power. After this entr'acte, the Spartans
declared war again in 413 and occupied the town of Decelea near Athens; with
Persian money, they built a navy and provoked revolutions in Athens'
possessions in Ionia. In 404, Athens surrendered..
|
B. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci, more commonly Leonardo da Vinci, was an Italian polymath whose areas of interest included invention, painting, sculpting, architecture, science, music, mathematics, engineering, literature, anatomy, geology, astronomy, botany, writing, history, and cartography.
| |
The Virgin of the Rocks (sometimes the Madonna of the Rocks) is the name used for two paintings by Leonardo da Vinci, of the same subject, and of a composition which is identical except for several significant details. The version generally considered the prime version, that is the earlier of the two, hangs in The Louvre in Paris and the other in the National Gallery, London. The paintings are both nearly 2 metres (over 6 feet) high and are painted in oils. Both were painted on wooden panel; that in the Louvre has been transferred to canvas.
| |
 |
The Virgin and Child with Saint Anne is an oil painting by Leonardo da Vinci depicting St Anne, her daughter the Virgin Mary and the infant Jesus. Christ is shown grappling with a sacrificial lamb symbolizing his Passion as the Virgin tries to restrain him. The painting was commissioned as the high altarpiece for the Church of Santissima Annunziata in Florence and its theme had long preoccupied Leonardo.
|
C. Noah and the flood
D. Others
Lysistrata

Lysistrata is a comedy by Aristophanes. Originally performed in classical Athens in 411 BC, it is a
comic account of one woman's extraordinary mission to end the Peloponnesian
War. Lysistrata
persuades the
women of Greece to withhold sexual privileges from their husbands and lovers as
a means of forcing the men to negotiate peace—a strategy, however, that inflames the battle between the sexes.
沒有留言:
張貼留言